The testicles play an important role in a man’s reproductive system. Also called testes, they are a pair of egg-shaped organs in-charge of producing testosterone and sperm. They are found inside the scrotum, behind the penis. Because they are not really protected by muscles or bones, they can easily be injured, especially when engaging in sports and other physical contact activities.
For the good health and wellbeing of your testicles, you should go see your doctor regularly for a testicle exam. It is important that yours are checked for any lumps, pain, redness, inflammations, or other changes that may signify something that requires medical attention.
Below are examples of common testicular diseases that can strike men:
1. Testicular Cancer
If you have testicular cancer, it means that there are abnormal cells in your testicles, and they are growing and dividing uncontrollably. You will develop a variety of symptoms, such as a lump, inflammation of one or both of your testicles, aching in the lower abdomen or groin, pain in the scrotum or one or both of your testicles, and a heavy, pulling sensation in the scrotum.
There are many risk factors associated with testicular cancer. If you have any of the following, your odds of getting the disease are higher:
- Undescended testicle
Undescended testicle, or cryptorchidism, is a condition characterized by the testicles not descending from a male’s abdomen to the scrotum before his birth.
- Family history of the disease
If you have a father, grandfather, an uncle, or someone in your family tree that has/had testicular cancer, you have a greater risk of having the disease than someone who does not.
- Aged between 15 and 40
Although testicular cancer can affect men at any age, those who are between the ages of 15 years old and 40 years old are more prone to it.
- Caucasian
According to studies, Caucasian men are five times more likely than African-American men, and two times more likely than Asian-American men to develop testicular cancer.
2. Epididymitis
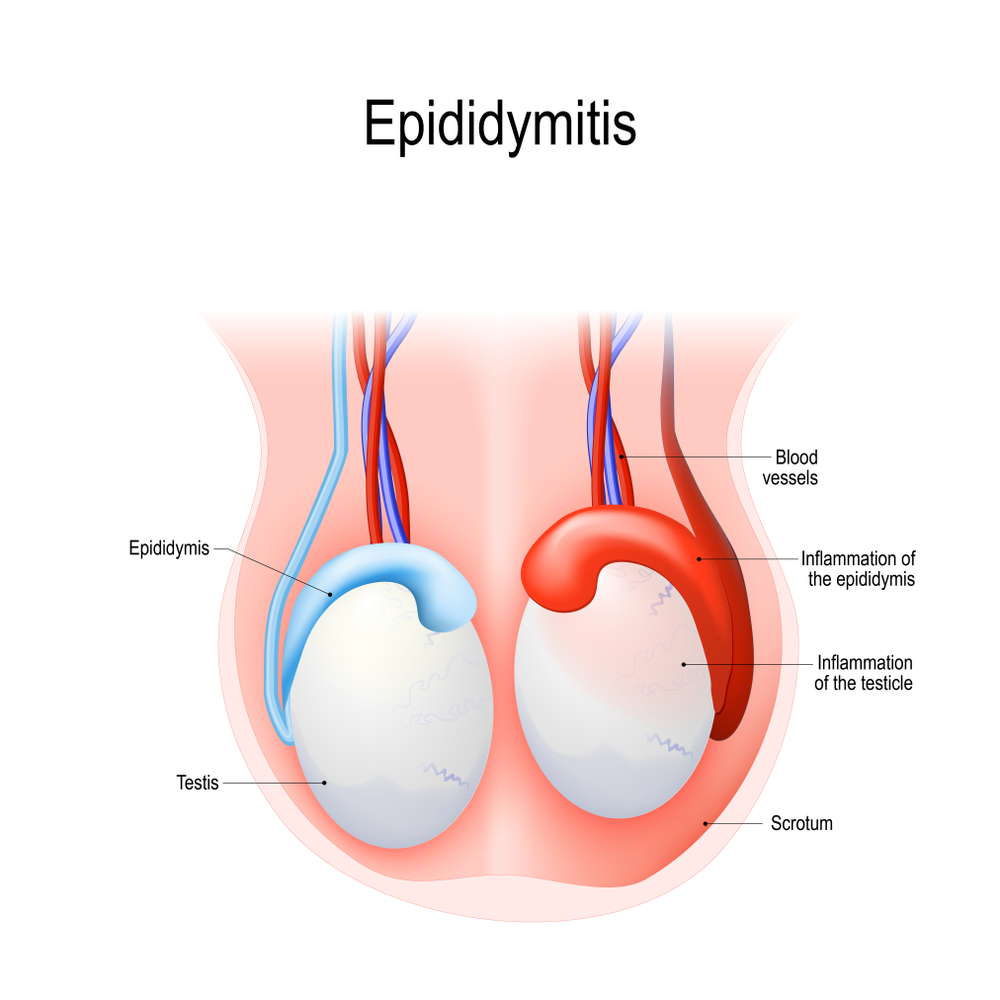
Frequently caused by Chlamydia, a very common sexually transmitted disease brought about by bacteria, epididymitis is a condition that affects the testicles. If you have it, you will experience a variety of signs and symptoms, such as inflammation of the testicles, pain in the scrotum, fever, and pus.
To treat it, you will be prescribed by your doctor antibiotics that can get rid of the bacteria that started the infection, and anti-inflammatory medications, like ibuprofen, to help ease the swelling and pain.
If not treated as soon as possible, epididymitis can lead to scar tissue, which can obstruct the pathway of sperm, blocking it from leaving your testicles. It can also cause infertility.
3. Testicular Torsion
Your testicles are kept in place inside your scrotum by a cord-like structure known as the spermatic cord. If this spermatic cord gets twisted, it is bad news. This can disrupt the blood flow to your testicles, and cause sudden and extreme pain, swelling, and tenderness.
Most common in men between 12 years old and 18 years old, testicular torsion is a disorder that can be caused by strenuous activities, injuries to the testicles, and, sometimes, even for no apparent reason. It requires emergency medical attention, and can be treated by correcting the torsion or twisting through surgery.
If diagnosed and attended to right away, you will not encounter any serious problems in your testicular functions. However, if not corrected as soon as possible, your testicles may suffer from permanent damage due to not receiving sufficient blood for an extended period of time. You may have to undergo surgery for the removal of your damaged testicles.
4. Testicular Trauma
If you are an athlete, you know how easy it is for your testicles to get hit, crushed, struck, or kicked. Oftentimes, because of the spongy structure of the testicles, the intensity of the shock or pressure they receive is minimized, so there is no resulting serious injury or damage.
However, in some cases, there can be bruising, swelling, or severe pain, especially if they receive a direct blow or squeezed too hard. This can then lead to blood leakage into the scrotum, which necessitates a surgical procedure. If done immediately, the rupture can be repaired, and your testicles saved.
5. Hypogonadism
The insufficient production of testosterone in a man’s body is a medical condition known as hypogonadism. It is typically caused by an abnormality or a problem in the testicles or pituitary gland. It can strike males at any age, from the fetal development stage to adulthood.
If you have it, you will experience different complications in your fertility and reproductive functions. The following are examples of such problems:
- Lower libido or sex drive
- Inability to get an erection or maintain an erection, also known as erectile dysfunction
- Decrease in body hair (chest hair, pubic hair, beard, etc.)
- Muscle loss
- Weight gain
- Enlarged male breast tissue
- Firmness or shrinking of your testicles
6. Varicocele
If the veins in your scrotum are enlarged, you have a disorder known as varicocele. It is comparable to the varicose veins that occur in the legs, and is not really very dangerous.
However, in rare cases, it can trigger mild to moderate aches and pains, lower your sperm quality and production, and affect your other sexual and reproductive functions.
7. Hydrocele
If there is swelling in your scrotum, you may have a disorder known as hydrocele. It is common in newborn babies, and occurs when there is fluid accumulating in the thin sheaths around the testicles, and then disappears even without treatment when they reach the age of 1.
In adult men, it can happen if there is injury or inflammation within the scrotum, or exposure to a sexually transmitted disease or other infections.
Even though hydrocele is not usually dangerous or life-threatening, it can be a sign that you may have an underlying condition that can progress to something a lot more serious, such as inguinal hernia or a tumor.







