Medications, such as beta-blockers, are made to treat various conditions, but they come with unfavorable side-effects. And these medications might affect your hair, including changes in hair texture or color, excess hair growth, or hair loss.
Alopecia or hair loss is a condition that may affect both men and women due to genetics, health-related problems, and medications. Hair loss may just be a temporary side-effect of medication, but there are instances when this may result in a permanent hair loss like pattern baldness.
Some people might consider hair loss as a minor side-effect of taking beta-blockers, but others take it as a big deal. In this article, we will determine whether or not beta-blockers really cause hair loss. But first, we will know how drugs cause hair loss.
Why Beta-blockers Cause Hair Loss?
Hair loss occurs when the normal cycle of the growth of your scalp is interfered with by the drugs you take; in this instance, beta-blockers. There are three phases of the cycle of scalp hair growth- the anagen, catagen, and telogen phases, respectively.
The hair grows for about six years during the first phase. After that, the hair rests about three months to prepare for the last phase. During the telogen phase, hair loss occurs, but this is replaced by newer hairs.
Telogen effluvium and anagen effluvium are the two types of hair loss due to medications, such as beta-blockers. Telogen effluvium or short-term and temporary hair loss usually occurs within 2 to 4 months after taking beta-blockers.
This drug causes the hair follicles to proceed to the resting phase, which makes hair fall out too early. People with this kind of condition shed about 30 to 70 percent more than the normal hair fall a day.
On the other hand, anagen effluvium or long-term hair loss occurs during the anagen phase when the matrix cells are prevented from dividing normally. These cells are responsible for producing new hair.
After a few days or weeks of taking medications, hair loss happens. This is common if you are taking chemotherapy drugs for cancer. But a study has included beta-blocking agents to cause this condition. Anyway, the severity of hair loss due to medication depends on the dosage of the beta-blockers, as well as your sensitivity to the same.
Beta-blockers That Cause Hair Loss
Beta-blockers are commonly prescribed to treat hypertension. It works by slowing down your heart rate, which decreases your heart’s demand for oxygen. Beta-blockers are also good to treat other heart-related conditions such as heart failure, abnormal heart rhythms, heart attack, and angina. Taking beta-blockers may come with some side-effects such as hair loss.
Beta-blockers include propranolol, metoprolol, labetalol, atenolol, nadodol, and timolol.
Propanolol
A study has shown that propranolol, a kind of beta-blocker, can result in hair loss. However, this kind of hair loss is merely temporary. This is caused by the hair follicles to prematurely proceed to the shedding phase as aggravated by the medication.
Metoprolol
Taking metoprolol can cause reversible alopecia. Reversible means that it can be back to what it previously was. Although hair loss is experienced while taking metoprolol, chances are the hair will grow back after you stop the said medication.
Labetalol
Hair loss is a rare complaint when taking labetalol. It was reported that only less than 1 percent of users experience this problem. And if in case hair loss occurs, this is usually reversible. It means that your hair will just grow back after you stop taking this medication.
Atenolol
Drastic hair loss may be experienced if you are taking atenolol for high blood pressure. This is one of the known side-effects of taking beta-blockers. One of the ways to prevent hair loss is to ask your doctor to switch to another beta-blocker that can treat the same condition without the risk of alopecia.
Nadolol
Nadolol users do not experience serious side effects. And one of the serious side effects of this medication is hair loss. Taking nadolol can result in reversible hair loss. You need to seek help from your doctor if you experience this condition.
Timolol
Timolol is a beta-blocker that may result in adverse dermatological effects, including alopecia. A limited number of patients reported that timolol induced telogen effluvium, resulting in the shedding of hair from the scalp, eyelashes, and eyebrows. This happens within 1 to 24 months after taking timolol.
Treating Drug-Induced Hair Loss

You should ask your doctor about the possible side effects of taking beta-blockers. If hair loss occurs due to this drug, your hair will just grow again after you stop taking beta-blockers. But if stopping the medication does not improve hair thinning, you may need treatment for hair loss such as minoxidil or finasteride. These are medications that can help stimulate hair growth.
If medications are not effective, you may be asked to undergo surgery to improve hair growth and reduce hair loss. But this option can be painful and quite costly. There are also non-medical solutions for hair loss, such as lifestyle changes and home remedies. Some people who experienced great hair loss use a wig, a hairpiece, or scarves.
Conclusion
Beta-blockers can cause hair loss as one of the side effects of taking these drugs. But these are just rare instances, and hair loss is usually reversible. It only means that your hair will regrow on its own after you stop taking this medication. If you find hair loss bothersome, seek help from your doctor. He might prescribe another beta-blocker that will not result in hair loss.
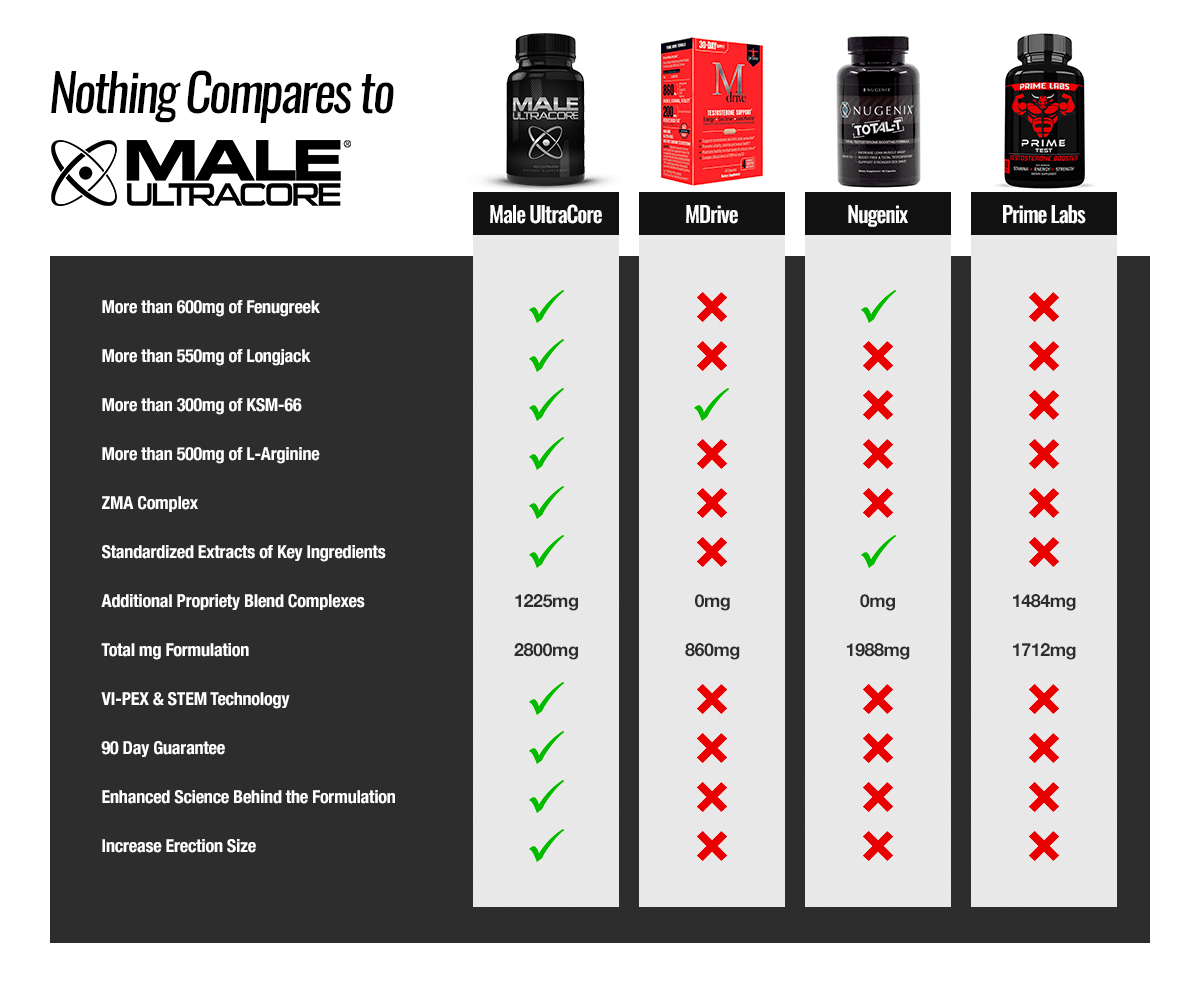
Increase Your Testosterone Levels with Testosterone Boosters
Male UltraCore is a premium testosterone boosting supplement that is designed to maximize test levels, increase your performance and drive, and give you harder and fuller erections.